In fact, the balance sheet lists assets in order of how liquid they are, starting with those with the highest liquidity (cash). The order of liquidity refers to the sequence or arrangement of assets and liabilities on a company’s balance sheet based on their liquidity. Liquidity refers to how quickly an asset order of liquidity can be converted into cash without affecting its market price, or how soon a liability needs to be paid.
Accounting for Current Assets
- Some of its receivables might not be included in the current assets account if a business makes sales by offering longer credit terms to its customers.
- The next on the list are marketable securities like stocks and bonds, which can be sold in the market in a few days; generally, the next day can be liquidated.
- Finally, intangible assets are at the bottom of the list because they are the least liquid and can take longer to convert to cash.
- In general, having a high amount of cash or cash equivalents indicates a high level of liquidity.
- The business credit card transactions which are not yet paid must be reported as an accrued liability.
Current assets are always located in the first account listed on a company’s balance sheet under the assets section. Apple, Inc. lists several sub-accounts under current assets that combine to make up total current assets. Current assets are short-term resources that can be used or converted to cash within one year or one operating cycle, whichever is longer. Non-current assets are long-term assets that a company expects to use for more than one year or operating cycle. They are called current assets because they can be converted into cash within 12 months. Businesses rely on these liquid resources to cover payroll, restock inventory, or capitalize on supplier discounts without incurring expensive debt.
- Recall that the days’ sales in inventory was one of the two components of a company’s operating cycle.
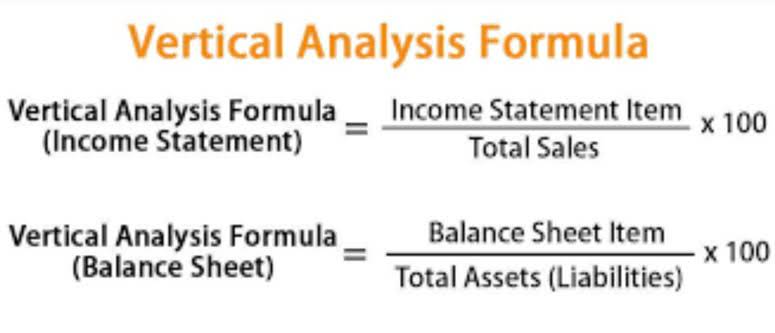
- The balance sheet is a part of a financial statement that presents the company’s assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity at a particular point in time, thereby providing insights into an entity’s financial position.
- The acid-test ratio, also known as the quick ratio, is a critical measure of a firm’s liquidity, assessing its ability to meet short-term obligations without relying on inventory sales.
- If the revenues come from a secondary activity, they are considered to be nonoperating revenues.
- Accurate valuation of trade receivables is crucial for maintaining the integrity of financial statements and adhering to accounting standards.
Cash

If a manufacturer turns its inventory six times per year (every two months) and allows customers to pay in 30 days, its operating cycle is approximately three months. The balance sheet reports the assets, liabilities, and owner’s (stockholders’) equity at a specific point in time, such as December 31. The balance sheet is also referred to as the Statement of Financial Position.
Inventory turnover ratio

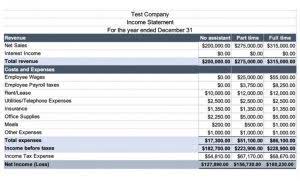
Highlighting the items that have more than 120 days’ sales in inventory may lead to action that will help the company. Perhaps some items haven’t been sold in the past year and should be sold at a clearance price or scrapped to save the costs of holding. Perhaps the method of calculating the future quantities to be purchased or produced should be improved. The 120 or 121.7 days of sales in inventory is an approximate average time needed to sell the average amount of inventory during the past year. Some Suspense Account products may have sold quickly because of high demand and some products may have been sitting without any units being sold during the year. Recall that the days’ sales in inventory was one of the two components of a company’s operating cycle.
🎓 Unlock Core Accounting Skills for Financial Analysts!
A current asset whose ending balance should report the cost of a merchandiser’s products awaiting to be sold. The inventory of a manufacturer should report the cost of its raw materials, work-in-process, and finished goods. The cost of inventory should include all costs necessary to acquire the items and to get them ready for sale. Accounts Payable is a current liability account that is credited when a company has received goods and/or services on credit terms. (The debit often involves an expense or asset account.) One practice is to credit Accounts Payable only after a three-way match has taken place.

Therefore, it helps in making informed judgements about the financial risk and creditworthiness of the company. Companies disclose the Current Assets they own and their values on the Balance Sheet. The one year period criteria is measured normal balance as 12 months from the date of the Balance Sheet.